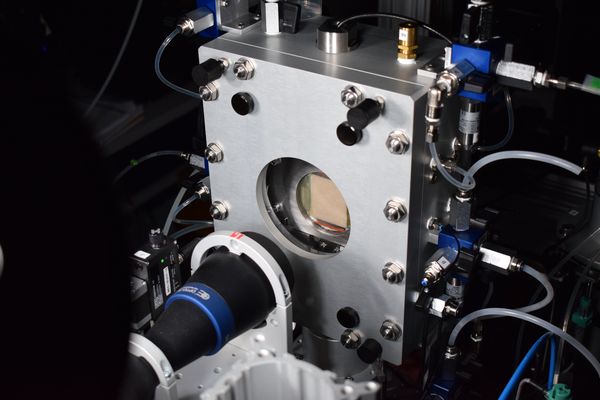
- Micro-scale approach: analysis of water flow through a granular medium based on the DEM (Discrete Element Method) and the LBM (lattice Boltzmann Method) methods.
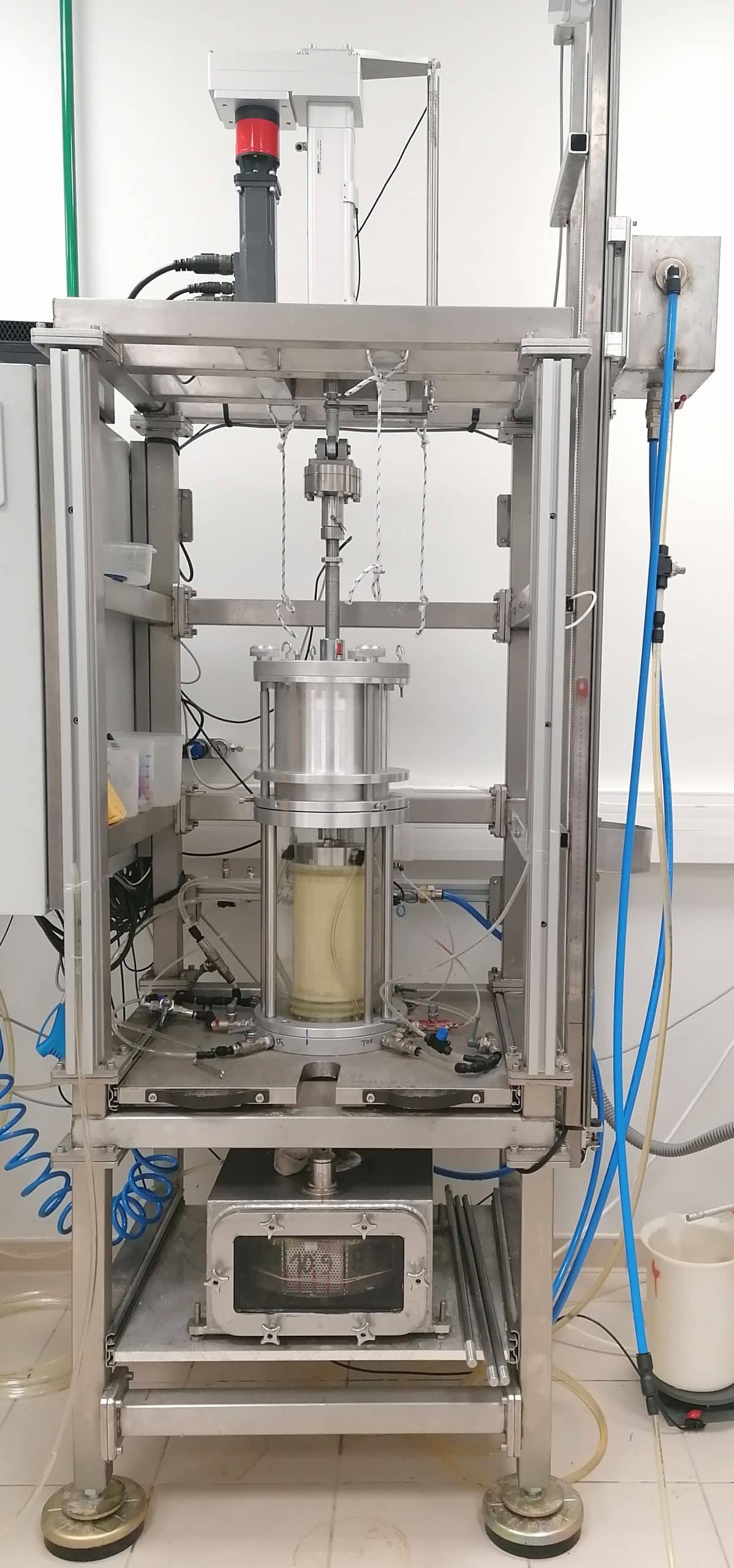
- Study of two-phase flows in soils through a biaxial machine for multi-phase interfaces allowing the live monitoring of strains and flow under biaxial loading and drainage/imbibition conditions. The goal is to reproduce at a laboratory scale the mechanisms of fluid infiltration and induced strains that can cause the rise of stored underground fluids, the pollution of the groundwater table, the precipitation of pollutants, etc.
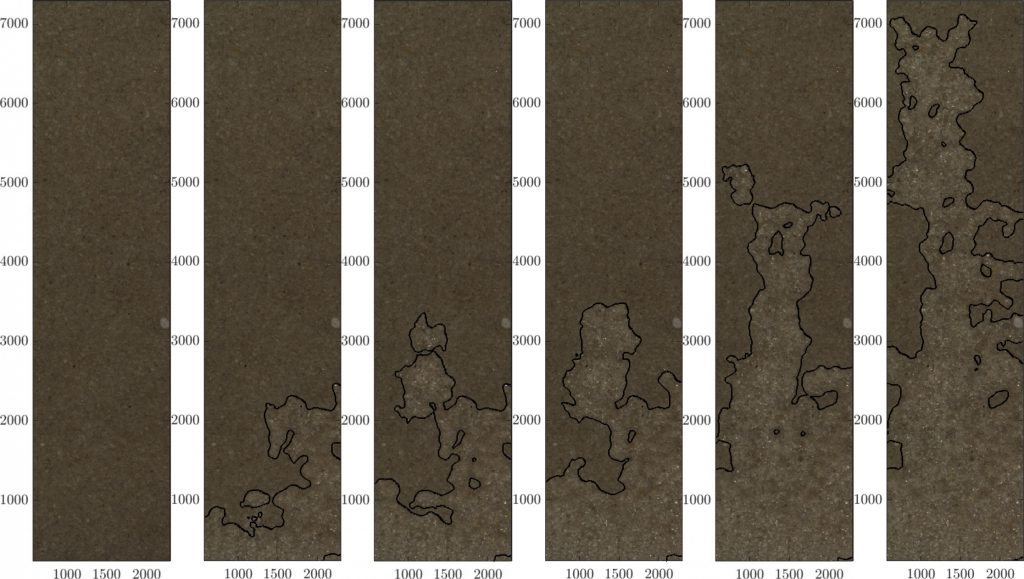
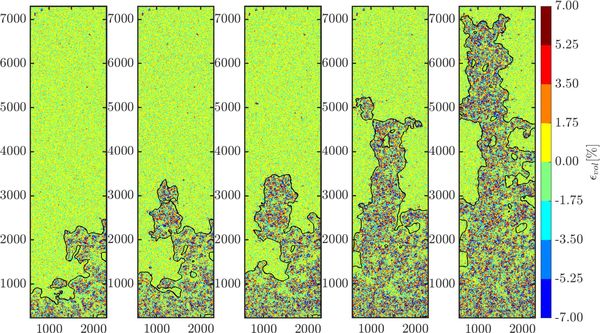
- Heterogeneous percolation (fingering) and map of induced volumetric strains, in drainage condition : air is injected through a sample initially saturated by water; strains are calculated through a digital image correlation algorithm (réf: Al Nemer R, Sciarra G and Réthoré J (2022) Drainage Instabilities in Granular Materials: A New Biaxial Apparatus for Fluid Fingering and Solid Remodeling Detection. Front. Phys. 10:854268. doi:10.3389/fphy.2022.854268)
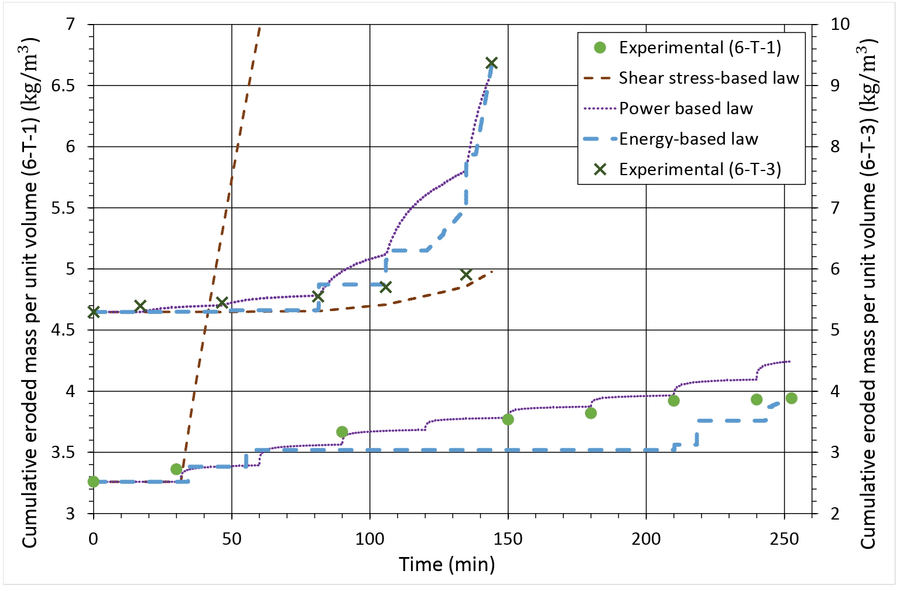
- Erosion by suffusion : laboratory-scale experimental study and modeling of a physical model of dike
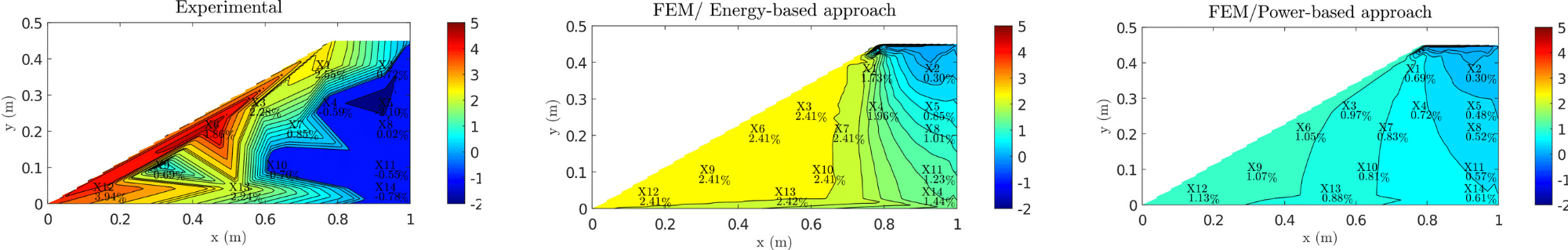
Spatial distribution of the variation of the percentage of fines after suffusion, with respect to the initial value of 25 %: (left) Experimental test, (middle) simulation with the energy-based relationship and (right) simulation with the power-based relationship.